OBD2 is used in the automotive industry to refer to the onboard diagnostics system. It has more advanced features than its predecessor obd1. An OBD-II compliant vehicle can use any of the five communication protocols: J1850 PWM, J1850 VPW, ISO9141-2, ISO14230 (also called KWP2000), ISO15765-4/SAE J2480.
Types of OBD2 protocols
Below are OBD2 protocols by vehicle make and model:
SAE J1850 PWM,SAE J1850 VPW,ISO 9141-2,ISO 14230 KWP2000,ISO 15765-4 CAN (SAE J2480)
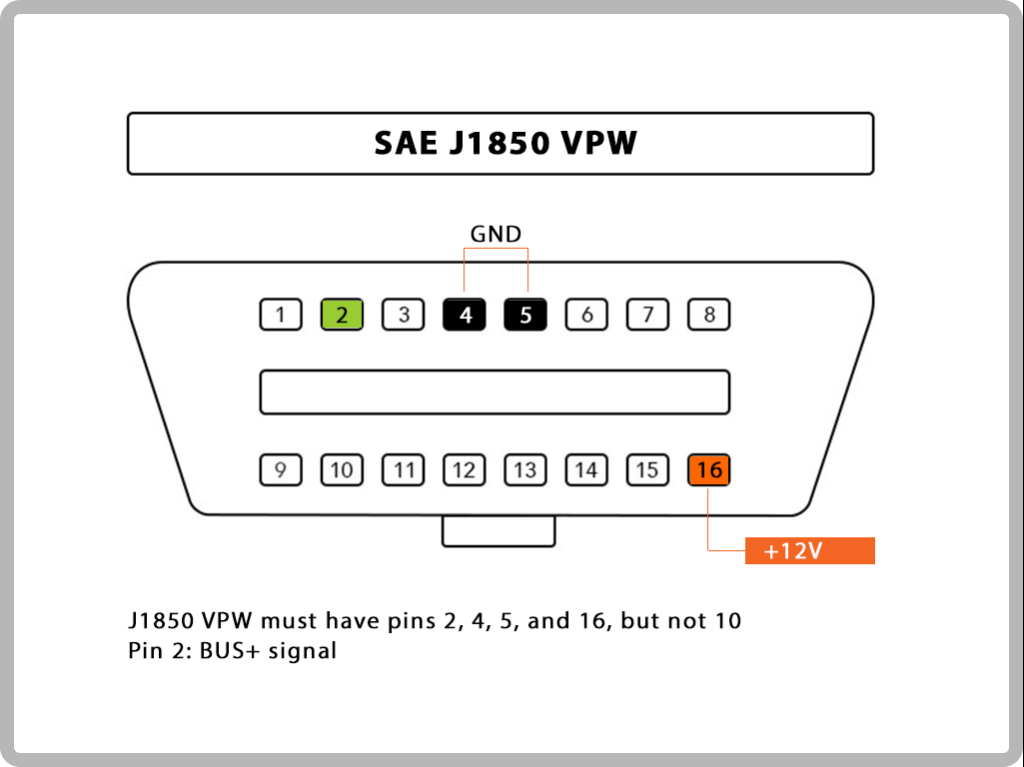
1.SAE J1850 VPW: This OBD2 protocol is used by Ford.
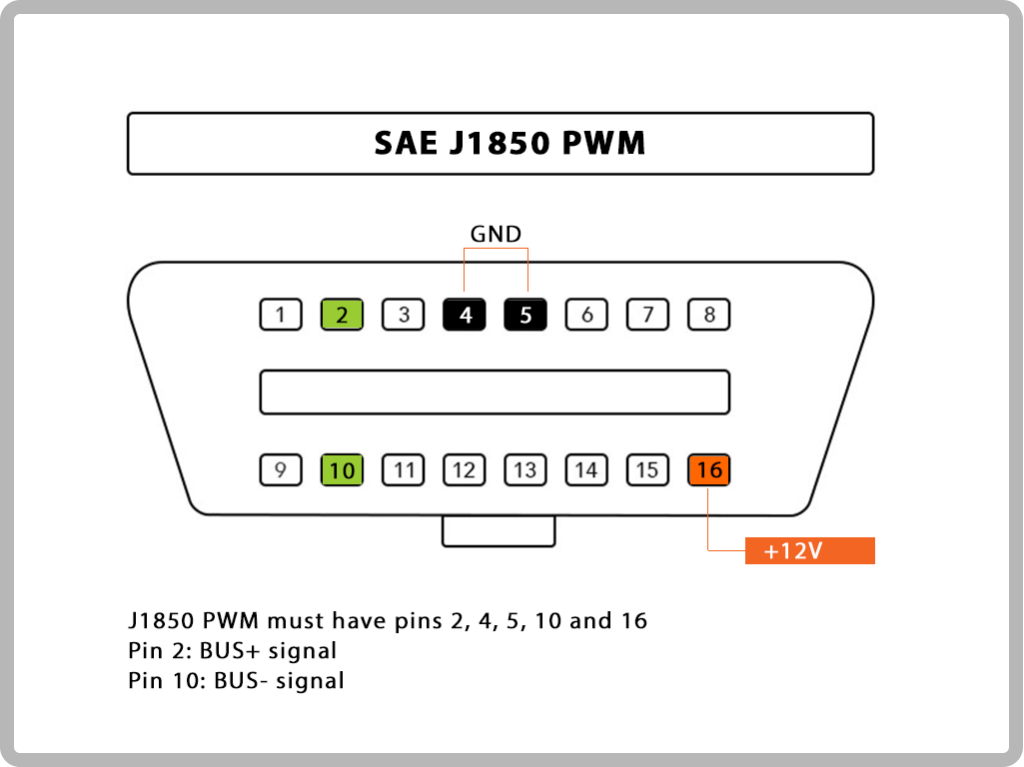
2. SAE J1850 PWM: Common Motors utilize this protocol.
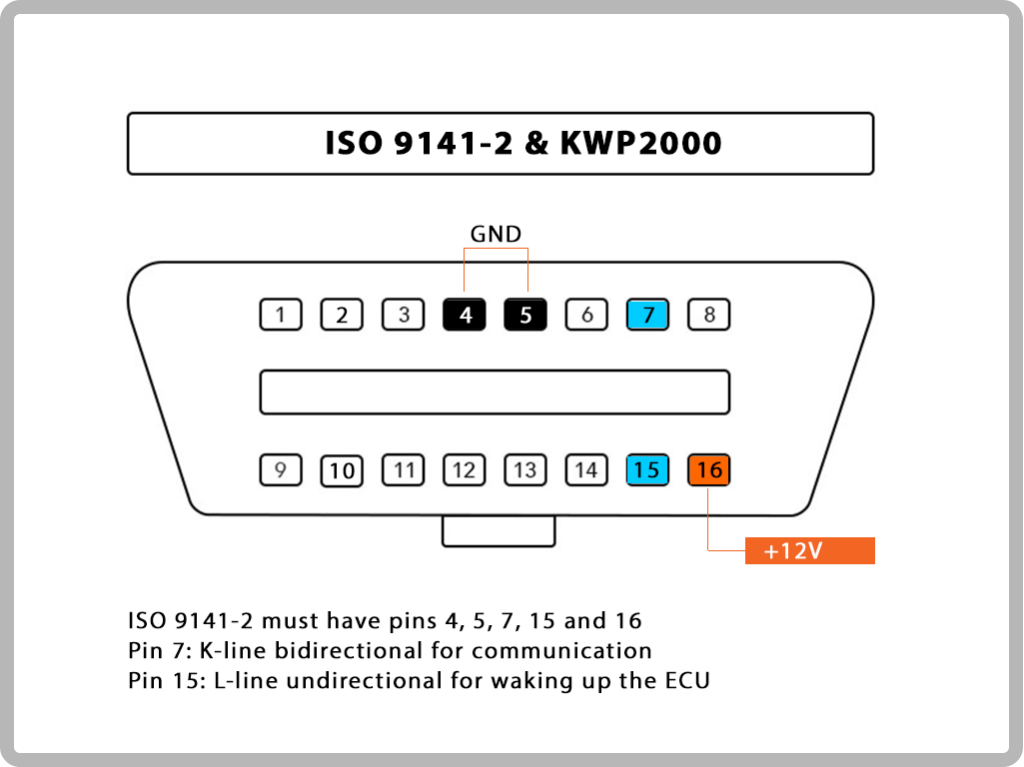
3. ISO 9141-2: You will find this protocol on Asian, Chrysler, and European cars.
4.ISO 14230 KWP2000: This protocol is found in Asian vehicles.
5. You will find this protocol in many vehicles made after 2008.
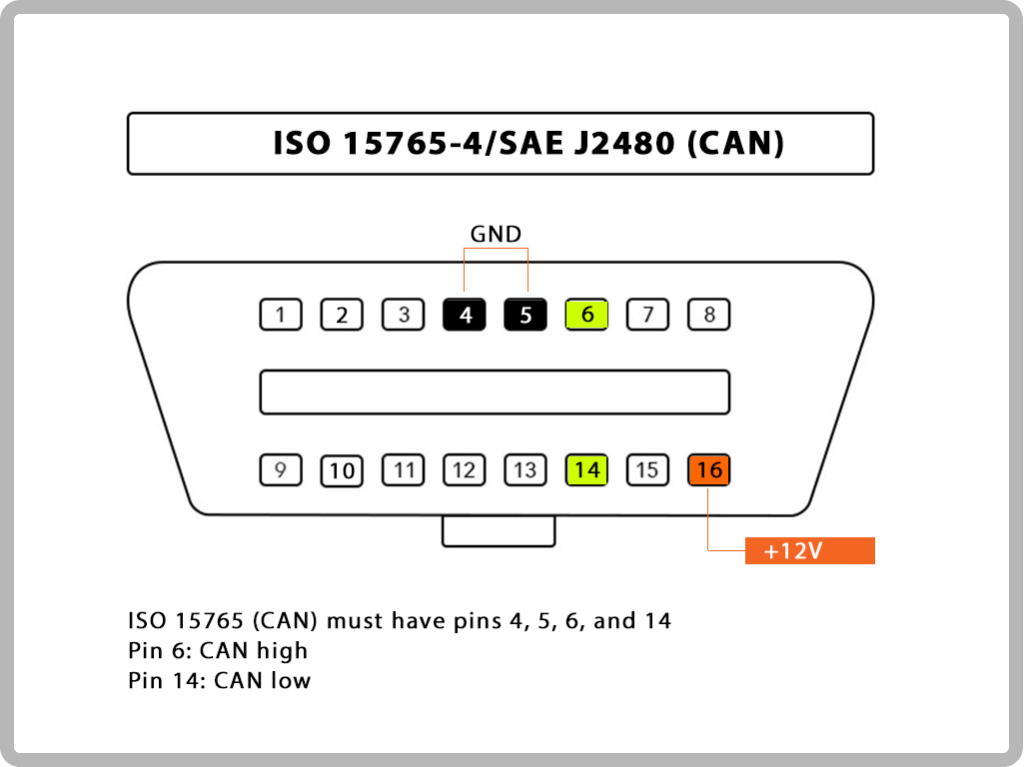
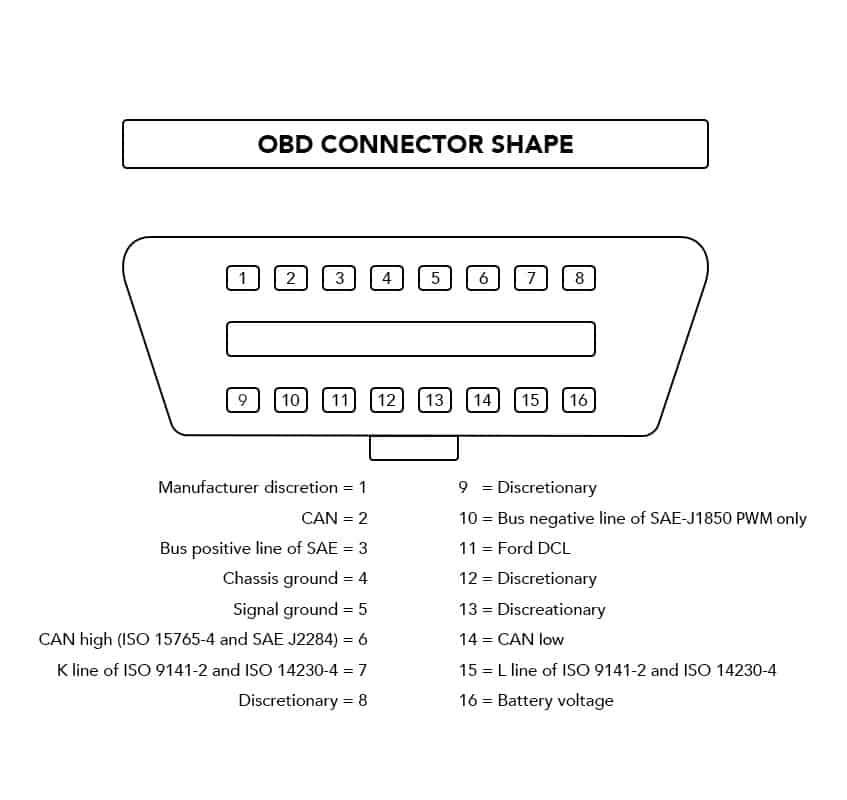
For most scanners, you just need an OBD2-compliant vehicle. You can normally use any scanner with any protocol. However, there are times when you want to be more specific. Not every OBD2 protocol connects with the scanner the same way. Unfortunately, the only way to know what protocol you have is to look at the pin datasheet of your vehicle’s connector.
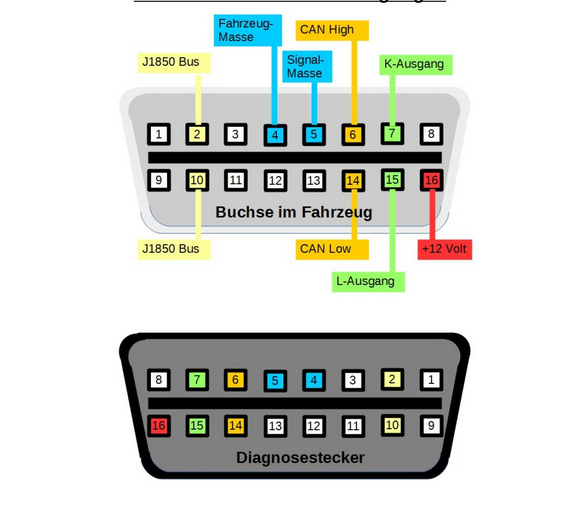
Top 8 Pins
1.Reserved for OEM COMM
2.J1850 Bus+ (positive)
3.OEM Reserved
4.Framework/car chassis ground
5.Sensor signal ground
6.OEM COMM / CAN High
7.K-line
8.OEM Reserved
Bottom 8 Pins
9.OEM COMM
10.J1850 Bus- (negative)
11.OEM Reserved
12.OEM Reserved
13.OEM Reserved
14.OEM Reserved / CAN Low
15.L-line
16.Power out (12 volts)
17.The following table explains how to determine the protocol:

Leave a Reply